Monoclonal antibodies are a class of medicines that have transformed the way we prevent and treat diseases, from cancer and diseases of the immune system, to childhood viral infections. They are not chemical compounds, as most drugs are.
They are based on natural antibodies – these are proteins the body makes to protect against disease, but they are made in laboratories and mass-produced in factories. This is why they are sometimes referred to as "designer antibodies" – they are adapted to the disease they treat.
Antibodies are proteins produced by our immune system and are one of the body's most important defense mechanisms against disease. You can also get more information about antibodies via https://www.bosterbio.com/featured-products.
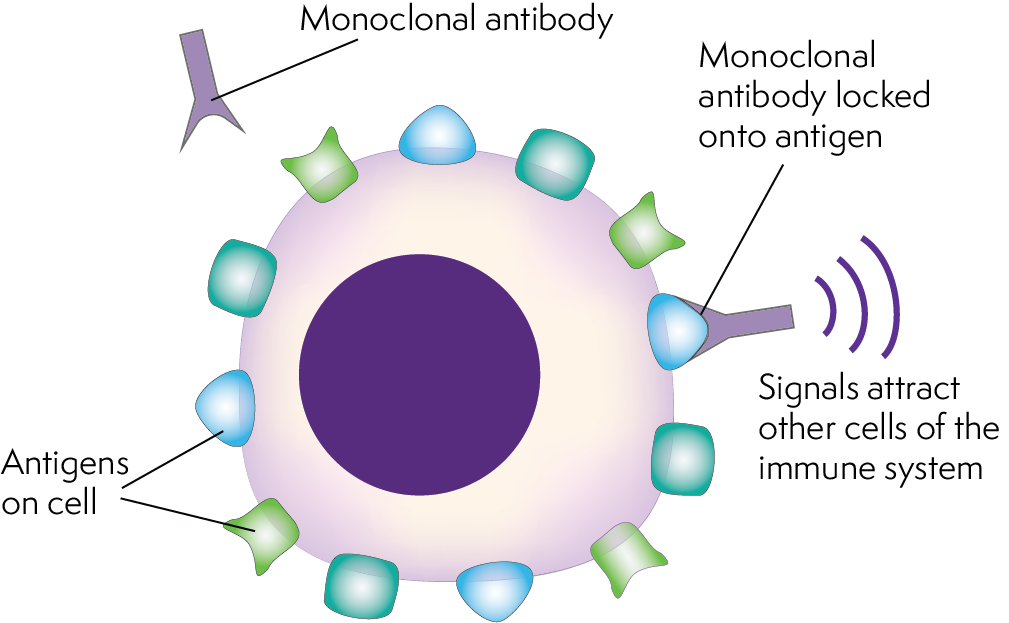
Image Source: Google
They work by linking to their specific targets – such as viruses, bacteria or cancer cells – and rendering them harmless. They block targets or mark them as foreign so that other parts of our immune system can clear the "intruder".
Monoclonal antibodies work the same way. They are committed to their specific goals without breaking anything in their path. The targets are not always "foreign intruders" like viruses.
Antibodies can be constructed in such a way that they attach to various molecules in the body, for example to weaken the immune response in the event of an overreaction; This phenomenon, which has also occurred in some Covid-19 patients, is known as a "cytokine storm".
Due to their wide range of applications, monoclonal antibodies are used safely and effectively to treat a growing number of diseases, some of which were difficult to treat in the past.